Climatic considerations as an integral part of planni ng. Here are several issues that would be treated differently in warm climates.
The buildings south face should receive sunlight between the hours of 900 AM.
. Winter weather or winter precipitation and its potential for hazardous conditions. Large projecting eaves and wide verandahs are needed in composite climate as out-door living areas to reduce sky glare keep out the rain and provide shades. Home Orientation Orient the house with the long axis east-west to minimize exposure to rising and setting sunlight.
Concepts of Passive Design in Composite Climate - ijresm. Design here are guided by longer prevailing climatic conditions. In composite climate the envelope should be designed so that it remains shaded for the greater part of the day.
Use north-facing high thermal mass living areas with passive solar. Light Buildings immediate surroundings other buildings trees etc location in the context Houses should be located behind a wind shield but be assured of exposure to the sun. Understanding Climate For Sustainable Building Design A Case Study In Warm Humid Region In India.
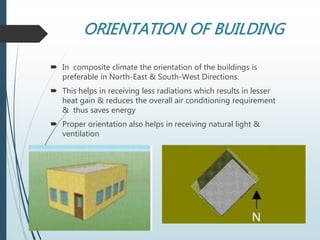
Design living spaces to face cooler facades. And 300 PM during the. This helps in receiving less radiations which results in lesser heat gain reduces the overall air conditioning requirement thus saves energy Proper orientation also helps in receiving natural light ventilation.
Climate-Responsive Design Conforming with 5 Apr 2013. Location of water bodies. In composite climate which material is mostly used - LandLearn NSW.
It minimizes the amount of heat transmitted into space in the hottest months while keeping heat inside during the cooler winter months. Energy Modeling Use energy modeling to optimize insulation air sealing and equipment selection. This is in view of the fact that buildings are designed and built without consideration for climate and the environment.
The key of design take an advantage of local climate microclimate for human comfort. It designs on the basis of climate considerations. The building should be elongated on an east-west axis.
Ensure adequate shading on the south side to cut off direct solar radiation during summers and permit winter sun. Passive solar systems basic rules-1. It takes up large amount of heat in evaporation and causes significant cooling.
The actual comfort conditions achieved will be contextual and depend on the building topology and building design specifications. Composite Impact of climatic factors on Building Design Topography Solar Radiation Wind Humidity Precipitation Sound Application in various Climatic Zones Building Design in Hot and Dry climate Planning Roofs and Walls Ventilation Traditional shelter Building Design in Warm and Humid climate Traditional Shelter Building Design in Composite climate. ORIENTATION OF BUILDING In composite climate the orientation of the buildings is preferable in North-East South-West Directions.
That said the purpose of this particular resource page is to bring awareness to one specific non-physical microclimate factor for consideration in design. Orient the buildings with longer axes in the east-west direction. Orientation is the most basic and prominent element to consider while designing in a hot and dry climate.
Get price Design Considerations for Making Composites. With reference to the same the prompted design considerations vary with existing structures contextual typologies and nature itself but the most prominent of all is the location of study and build. CLIMATIC CONSIDERATIONS JALIS.
Composite moderate and cold. Jalis on the outer facade of the building helps in cooling shading and ventialtion. It involves maximum use of sun and wind to make the building.
Below listed are 10 design considerations an architect must make while building in tropical climates. When designing three are the basic conciderations. CLIMATIC CONSIDERATIONS PROJECTIONS.
Orientation of the future buildings footprint entrances exits glazing interior spaces etc are prudently arranged and manipulated to create the most aesthetically pleasing efficient and. There are certain design considerations for composite region buildings which should resist heat gain in summer and resist heat loss in winter. This study therefore examines and.
And the sky conditions are againvariable which because it experiences all the 3 seasons. Water is a good modifier of micro-climate. The concept of climate-responsive design is related to green buildings and.
The passive design strategies for composite climate and also presents the various methods of passive cooling techniques. Design considerations Choose a site exposed to cooling breezes and design to exclude adverse winds while allowing for cross-ventilation and night purging. Window Considerations South facing facades should utilize a window area appropriate to its orientation and glazing should utilize a double or triple-paned glass with a Low-E coating.
Sun clouds orientation so as to benefit from the winter sun Wind Protection from winter winds. Their characteristics change from season to season alternating between long hot dry periods to shorter periods of. Now the physiological objectivefor composite climate becomes very difficult.
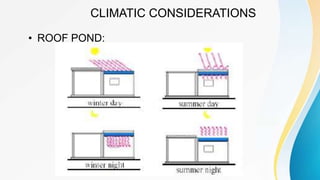
The climate resilience design considerations for each of those linked sections as well as additional climate resilience resources by section are included in this document for easy reference. CLIMATE RESPONSIVE DESIGN STRATEGIES IN COMPOSITE CLIMATE In passive solar energy mechanical means are not employed to utilize solar energy. So composite climate receives3 distinct seasons summers monsoons and winters and the conditions vary in each ofthese seasons which is what the problematic causes.
The orientation of the building should help in minimizing sun exposure during summer and provide warmth during winter for which the longer walls of the buildings should face the North and South and avoid west orientation. The external walls should be so planned that they shade each other. It do not involve mechanical and electrical energy.
There are certain design considerations for. Composite climate displays the characteristics of hot dry warm humid as well as cold climates.

Architectural Features Of Composite Climate In India

Design Of A Sustainable Residence In Composite Climate Of India


0 comments
Post a Comment